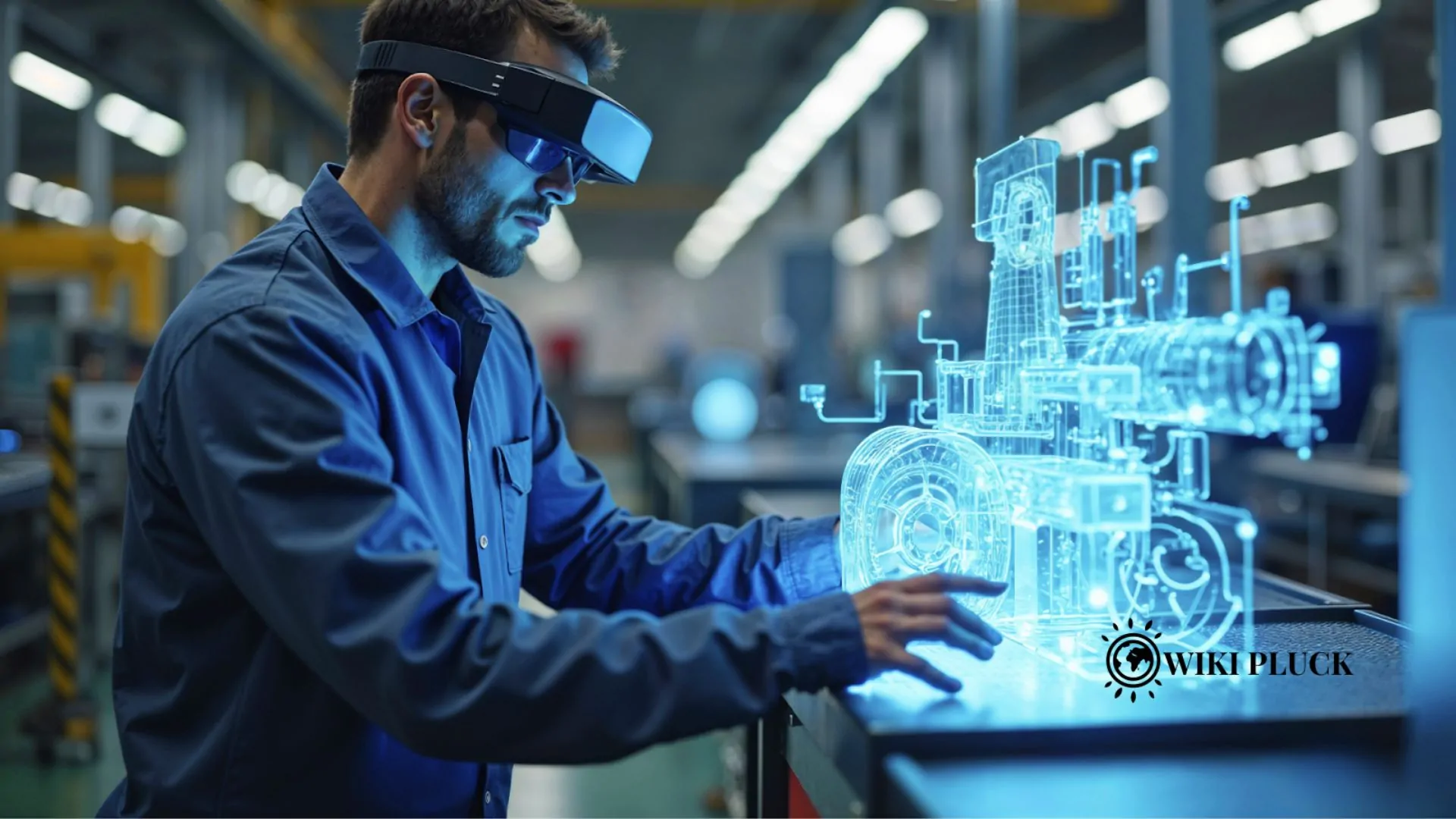
Unplanned downtime is the scourge of modern industrial operations. The latter is a single challenge that leads to operational cost, schedule insanity, as well as imposing immense complexity on the asset management. To the maintenance management experts and the plant leaders, the conventional method of repair after the fact or even preventive maintenance based on time is not quite sustainable in the 24/7 world. Remaining as a leader in the pack cannot be achieved by being better organized; it will require a change in approach.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is what is coming into play here, and it is a potent driver that is changing reactive and static maintenance into predictive, proactive and data-driven capability. AI is not only enhancing efficiency but is radically transforming the future of asset management. This guide will give a detailed tour of the way AI innovations can be utilized today to streamline operations, cut costs, and improve the reliability of assets to the maintenance managers and heads.
Understanding AI in Maintenance Management
AI is basically computers that can perform human intelligence processes such as learning, reasoning, and problem solving. In maintenance, this usually refers to Machine Learning (ML)- algorithms that analyze massive amounts of data to find and utilize patterns for predictions without any programming.
AI is not a stand-alone system as it is an important enhancement layer integrated into existing maintenance ecosystems. The computerized maintenance management system or enterprise asset management system possesses the historical data (work orders, repair logs, parts inventory) while the industrial internet of things feeds the real-time data from the sensors (vibration, temperature, pressure). AI treats this merged data stream in order to convert raw information into actionable intelligence.
Key AI technologies currently impacting maintenance include:
- Predictive Analytics: ML can be used to predict equipment breakdowns in time.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): An artificial means to ease human conversation and documentation giving a computer the ability to understand, interpret, and produce human language.
- Computer Vision: The cameras and AI analyze visual data to detect the defects and monitor safety.
Key AI Innovations Transforming Maintenance
In a highly proactive mentality, specific and integrated applications of AI propel the transition from being largely reactive. These innovations allow maintenance activities to be executed condition-based rather than regular or indefinite timing as not fixed, instead of guesswork.
- Predictive Maintenance (PdM) powered by AI
-
-
- How it Works: AI algorithms are trained on the large volumes of sensor data (vibration, temperature, oil quality) and repair history data to know the individual failure signature of every asset.
- Transformation: Rather than waiting until a system fails to recognize the issue or conduct maintenance periodically, AI predicts the exact likelihood of failure days or weeks early.
- Core Benefit: Minimized Unplanned Downtime and Tuned Resource Assignments; maintenance is done not before it is necessary, or even after it is done.
-
- Automated and Dynamic Maintenance Scheduling
-
-
- How it Works: AI-based optimization engines are run with real-time variables such as the condition of the machine, the availability and skill of technicians, the situation of part inventory, and all the production schedules.
- Transformation: Automation of the system transforms the maintenance calendar and effectively prepares the most productive timeframes and resource allocations, and prioritization of the most vital work according to the current risk.
- Core Benefit: Greater Availability of Assets and Workforce Productivity through the reduction of traveling time and the conflicts in the schedules.
-
- AI-Enabled Anomaly Detection
-
-
- How it Works: AI models constantly compare equipment parameters with a state of normal operation, which reveals slight, immediate changes and indicates an imminent error.
- Transformation: Is an active safety net, which notifies abnormal variability (e.g., a small pressure variation or a strange noise pattern) in real-time.
- Core Benefit: Fault Interception in Early Stages, to enable technicians to deal with small-scale problems such as lubrication problems or sensor drift before it turns into a large-scale high-cost failure.
-
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Maintenance Requests
-
-
- How it Works: NLP is used by intelligent interfaces and chatbots to interpret and process human text and voice input by technicians and operators.
- Transformation: Makes work order creation more manageable, creating standardized and searchable CMMS data out of non-structured text notes, and making parts identification faster.
- Core Benefit: Data quality in the maintenance system is enhanced, and there is less administrative friction and faster work order processing.
-
- Remote Assistance and Augmented Reality (AR)
-
- How it Works: The AI applications are used to operate virtual assistants and AR overlaid, display real-time diagnostics, step-by-step manuals on devices, and machine schematics straight onto the screen of technician in the field.
- Transformation: Empowers experts that are remote to instruct on-site employees on complicated or new repairs, without being concerned about geographical distribution.
- Core Benefit: Higher First-Time Fix Rates and Quickened On-the-Job Training by offering the necessary expertise at the appropriate time and location.
Also Read: How AI Is Redefining the Future of Maintenance and Asset Management
Benefits of AI-Driven Maintenance Management
The implementation of AI technologies is a game-changer that positively impacts the bottom line and is felt by the whole maintenance and operations ecosystem, which should make its assets as valuable as possible.
- Significant Cost Reductions
-
-
- Eliminate the high-cost emergency fixes by avoiding disastrous breakdowns.
- Minimize the expenditures on premium shipping of urgent parts, holding costs in the form of spare parts inventory and overtime technicians.
-
- Enhanced Equipment Lifespan and Reliability
-
-
- Implement very specific remedies in case of small problems in their emergence, to avoid straining the asset and its early deterioration.
- Ensure greater reliability and availability of assets through reactive fixes to optimal and prescriptive fixes.
-
- Improved Decision-Making and Planning
-
-
- Gain predictive insights to measure how risky the failure will be and transition from intuitive decision-making to data analytics.
- Elaborate resource allocation and budget requests with leaders of maintenance should be made with clear and evidence-based justification.
-
- Increased Workforce Productivity
-
-
- Automation of low-value, routine processes, such as the creation of work orders and the optimization of schedules, relieve skilled technicians.
- Wrench time can be enhanced if technicians can reach the asset with the identification of the diagnosis, parts, and tools characterized by AI.
-
- Safety Improvements and Risk Mitigation
-
- Recognize hazardous conditions such as high heat, gas leaks, or any structural defects ahead of human reach.
- Minimize the rate of maintenance activities in high-risk emergency conditions.
Integrating AI with CMMS and IoT
To unlock the power of AI, it must collaborate with already existing data sources and systems of execution. This combination fosters the closed-loop maintenance environment in the form of Industry 4.0.
- How AI Enhances CMMS Capabilities
-
-
- Automation: AI will change detailed predictive alerts and pre-populate work orders in the CMMS for high priority automatically, thus deleting manual transcription and decision delay.
- Accuracy: Prescriptive AI analyses will be able to say the right things (e.g., Replace bearing B does not motor altogether), thus improving repair choice accuracy in CMMS.
- Decision Support: CMMS transforms a passive historical ledger into an active decision-support system that uses the insights of AI to implement the dynamic allocation of resources and optimize workflows.
-
- Role of IoT in Providing Real-Time Data for AI Algorithms
-
-
- The Data Fuel: The Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) offers data that is of necessary velocity and contains the required data to fuel the AI engine. This contains live feeds on sensors that check vibration, acoustic emissions, temperature, pressure, and power consumption.
- Contextualizing Health: IoT data gives the AI the capacity to contextualize the health of an asset not only depending on the failures it has had in the past (CMMS data) but also its current operational state, which facilitates immediate and accurate predictions.
- Edge Computing: In many cases, IoT gateways utilize the first AI models on the network edge to filter data, which only important and processed information reaches the CMMS/cloud to have further ML processing.
-
- Examples of Seamless AI, CMMS, and IoT Integration for Unified Asset Management
Closed-Loop Prediction-to-Action: A sensor of the IoT identifies a suspicious vibration pattern. The AI option interprets the data and forecasts failure within 7 days and automatically submits an urgent and high-priority work order to the CMMS. The CMMS will then send the job to the most qualified technician and will reserve the required parts.
Condition-Based Inventory: AI tracks the expected component life of all assets and re-entered the risk back to the CMMS/ERP to optimize the spare parts inventory and sends a replenishment order only when the component is likely to be utilized.
Digital Twins: AI models Digital twins (a virtual copy of an asset) are continually updated with real-time data of the IoT. This enables the managers of maintenance to provide virtual reality of the impact of the planned repair or change of operations before making a physical approach to the practice.
Also Read: Business Finance Trends for Smart Entrepreneurs in 2025
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting AI
The implementation of AI should be planned with maintenance leaders taking the initiative to deal with major organizational and technical obstacles. It is paramount to acknowledge these challenges and discuss reducing measures that would ensure the successful transition process.
Data Quality and Integration Complexities
- The Challenge: AI models require clean, complete, and consistent data. The old CMMS systems can have discrepancies in history and data is often isolated in various working systems (e.g., ERP, SCADA) to make it hard to analyze.
- The Solution: Pre-deployment priority should be a data governance strategy. This includes cleaning historical CMMS data, setting standard data collection procedures for all new sensor inputs, and the creation of single data lakes to eliminate silos.
Change Management and Workforce Training
- The Challenge: The employees of maintenance can be quite resistant to AI-based suggestions or can distrust them because they see the introduction of AI-based solutions as a threat to their professional skills or even employment.
- The Solution: Take a massive investment in specific training that is aimed at data literacy and cooperation with AI tools, not substitution. Assign the AI as a strong ally, an augmented intelligence tool and take the essential technicians through initial validation stages to instill trust and ownership.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Concerns
- The Challenge: Extending the sensor networks (IoT) and transmitting sensitive data about the operations to the cloud-based artificial intelligence platforms increases the digital attack surface of the organization, and it creates new cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
- The Solution: Introduce strong endpoint security of all IoT sensors and devices. Encrypt all data sent and stored in accordance with industry data privacy standards to safeguard proprietary operational information, as well as the integrity control system.
Future Trends and Innovations in AI for Maintenance
The field of AI is constantly being innovated, and even greater transformative power of the maintenance management can be expected. These are the major trends that maintenance leaders ought to observe in order to future-proof their operations and technology roadmaps.
Key Areas of Advancement
Deep Learning for Hyper-Accurate Predictions
- The Trend: In the future, it will be necessary to go further than usual Machine Learning and employ Deep Learning (DL) models (e.g., neural networks) that are more efficient in processing rather complex multi-dimensional sensor data (high frequency vibration, audio signatures).
- Impact: Allows significantly smaller, non-linear failure patterns to be identified sooner than was previously achievable, resulting in more dependable and timely warnings and minimizing false positives.
Expansion of Mobile AI and Edge Computing
- The Trend: Implementing advanced, low-weight AI code directly on field devices and sensors and mobile applications (Edge Computing).
- Impact: It facilitates the rapid and decentralized analysis of data and diagnostics in the source. This will guarantee real-time and situational information to field technicians, less dependency on tenuous cloud connectivity, and latency.
Generative AI for Maintenance Documentation and CMMS Implementation
- The Trend: Large language models (such as the Generative AI) are being used to generate, process, and summarize complicated documentation.
- Impact: Automates the generation of quality, standardized Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), reduces the number of pages in long repair records into data to act on, and simplifies the data population process when new CMMS is being implemented.
Conclusion
The journey of AI has been from futuristic thought to the present-age gigantic powerhouse of industrial efficiency and reliability of assets.
By the very nature of providing prescriptive insights and automating decisions of complex nature, these technologies put an end to the everlasting nightmares of downtime and operational costs.
Maintenance leaders must embrace these technologies, which enable a shift away from the traditional paradigm of reactive repairs towards a proactive approach of performance guarantees, thereby ensuring a resilient and optimized future for their operations.
FAQs
What is AI-driven predictive maintenance and how does it work?
Machine-learning algorithms applied to massive amounts of data to analyze sensor data (vibration, temperature, oil quality, etc.) and historical repair records with the goal of detecting pattern changes that may be signatures for imminent asset failure are said to form the basis of AI-driven predictive maintenance.
In essence, the actual probability of failure may then be determined day-to-week prior, allowing maintenance activities to occur prior to breakdowns instead of after, as seems to be the logic with periodicals or reactivity.
How does AI improve maintenance scheduling and workforce productivity?
The intelligence in artificial systems now encapsulates scheduling maintenance using real-time variables like machine state, technician availability and skills, parts inventory, and production schedules.
Thus, creating a list of dynamic, prioritized works orders, which help better allocation of resources while reducing assets’ downtime, traveling time, and scheduling conflicts, with an increased performance of the workforce.
What are the main benefits of integrating AI with CMMS and IoT?
This system will give way to live supervision of asset health and deliver predictive alerts. AI can then automatically generate work orders into the CMMS and prescribe analyses to aid management and condition-based decisions in their inventory optimization processes.
The speed of the sensor data provided by the IoT is what will drive the accuracy of the prediction done by the AI, while edge computing will work towards filtering the data in its initial format for a faster response.
What challenges come with adopting AI in maintenance management?
A few challenges would have to be encountered, such as achieving high-grade, reliable information across the various legacy systems; overcoming fear, resistance from the workforce, and sufficient training in these tools to set trust in their application by means of their own experience; and tackling issues associated with the growing threat of cybersecurity, given digital connectivity and data transmission from IoT devices. Efficiency in data governance, change management, and enforced security will be vital for any success.
What future trends in AI will impact maintenance management?
The future trends include the use of deep learning models that will allow precise and early detection of failures, the rise of mobile AI and edge computing for decentralized real-time diagnostics, and generative AI for the automated production of maintenance documentation and simplified CMMS implementation.
All these trends will blindfold the maintenance functions with advancements toward even more proactive, efficient, and intelligent maintenance operations.

Passionate about cutting-edge technology and its role in Industry 4.0, I explore AI, Machine Learning, Big Data, and IoT to uncover their transformative potential. Excited to share insights, spark discussions, and learn from others as we shape the future of modern industries together.